Last Updated on May 11, 2023
The GNU Core Utilities or coreutils is a package of GNU software containing implementations for many of the basic tools, such as cat, ls, and rm, which are used on Unix-like operating systems.
Every day, we use many command-line tools to manage our systems, and perform basic tasks. Many of the programs provided by coreutils are staples in our daily life. Over the years, these tools have been updated and ported to other systems, but they still retain many of their original traits.
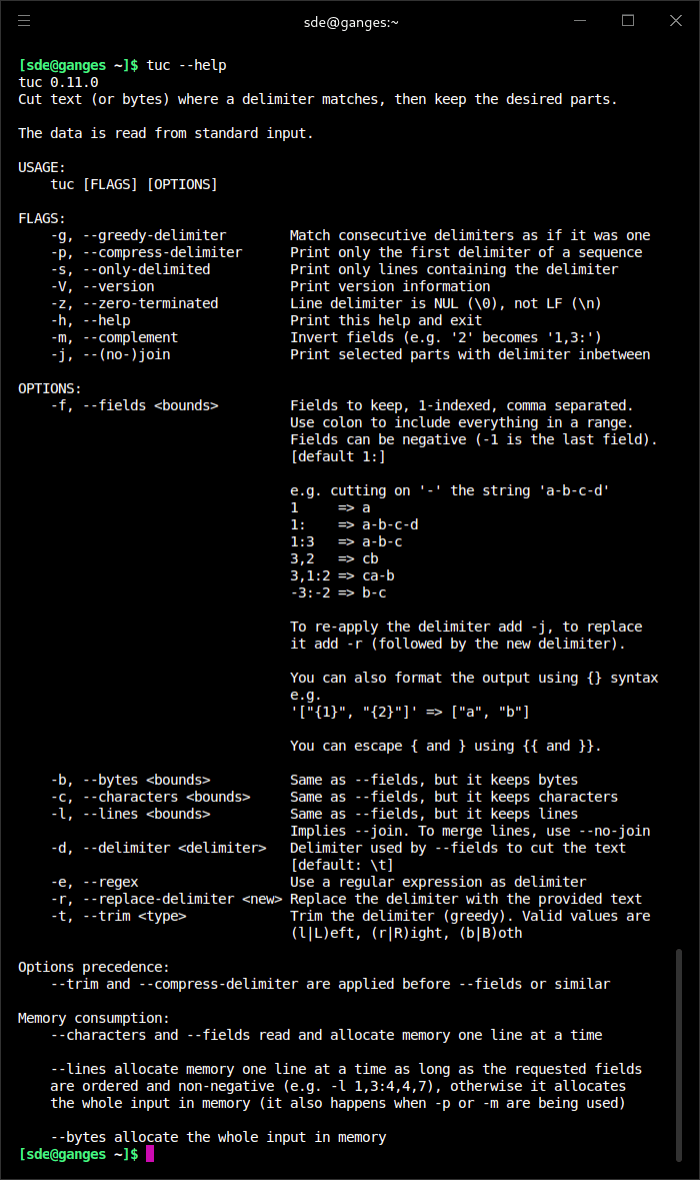
cut is one of the many utilities included with coreutils. cut writes to standard output selected parts of each line of each input file, or standard input. This lets us extract elements by defining ranges, delimiting characters and bytes. It’s not as widely known as some of its counterparts but it can still be a useful and practical command-line utility. cut doesn’t offer sophisticated field processing, like reordering fields, and handling fields aligned with blank characters.
tuc is a similar tool to cut but offers additional functionality. It allows us to split text or bytes into parts and reassemble them in any order. Parts can be referenced by negative indexes, and delimiters can be any number of characters long. It is particularly strong at extracting data from comma-separated lists.
Summary
tuc is a more powerful replacement for cut. It’s just reached it’s 1.0.0 release with this release having the regex feature enabled by default for the first time. The developer now provides tuc-lite which is tuc without regex support..
The project provides pre-built binaries for Linux (Ubuntu), macOS, and Windows. But it’s trivial to compile the source code.
Website: github.com/riquito/tuc
Support:
Developer: Riccardo Attilio Galli
License: GNU General Public License version 3.0
tuc is written in Rust. Learn Rust with our recommended free books and free tutorials.
For other useful drop-in replacements for coreutils, explore our roundup.
| Popular series | |
|---|---|
| The largest compilation of the best free and open source software in the universe. Each article is supplied with a legendary ratings chart helping you to make informed decisions. | |
| Hundreds of in-depth reviews offering our unbiased and expert opinion on software. We offer helpful and impartial information. | |
| The Big List of Active Linux Distros is a large compilation of actively developed Linux distributions. | |
| Replace proprietary software with open source alternatives: Google, Microsoft, Apple, Adobe, IBM, Autodesk, Oracle, Atlassian, Corel, Cisco, Intuit, SAS, Progress, Salesforce, and Citrix | |
| Awesome Free Linux Games Tools showcases a series of tools that making gaming on Linux a more pleasurable experience. This is a new series. | |
| Machine Learning explores practical applications of machine learning and deep learning from a Linux perspective. We've written reviews of more than 40 self-hosted apps. All are free and open source. | |
| New to Linux? Read our Linux for Starters series. We start right at the basics and teach you everything you need to know to get started with Linux. | |
| Alternatives to popular CLI tools showcases essential tools that are modern replacements for core Linux utilities. | |
| Essential Linux system tools focuses on small, indispensable utilities, useful for system administrators as well as regular users. | |
| Linux utilities to maximise your productivity. Small, indispensable tools, useful for anyone running a Linux machine. | |
| Surveys popular streaming services from a Linux perspective: Amazon Music Unlimited, Myuzi, Spotify, Deezer, Tidal. | |
| Saving Money with Linux looks at how you can reduce your energy bills running Linux. | |
| Home computers became commonplace in the 1980s. Emulate home computers including the Commodore 64, Amiga, Atari ST, ZX81, Amstrad CPC, and ZX Spectrum. | |
| Now and Then examines how promising open source software fared over the years. It can be a bumpy ride. | |
| Linux at Home looks at a range of home activities where Linux can play its part, making the most of our time at home, keeping active and engaged. | |
| Linux Candy reveals the lighter side of Linux. Have some fun and escape from the daily drudgery. | |
| Getting Started with Docker helps you master Docker, a set of platform as a service products that delivers software in packages called containers. | |
| Best Free Android Apps. We showcase free Android apps that are definitely worth downloading. There's a strict eligibility criteria for inclusion in this series. | |
| These best free books accelerate your learning of every programming language. Learn a new language today! | |
| These free tutorials offer the perfect tonic to our free programming books series. | |
| Linux Around The World showcases usergroups that are relevant to Linux enthusiasts. Great ways to meet up with fellow enthusiasts. | |
| Stars and Stripes is an occasional series looking at the impact of Linux in the USA. | |
