Disk partitioning is the means of dividing a hard disk drive into multiple logical storage units referred to as partitions. A partition is a contiguous set of blocks on a drive that are treated as an independent disk.
There are many benefits of having multiple partitions on a disk. One of the most popular reasons is to separate the operating system and program files from user files. Many Linux users prefer having the /home directory on a separate partition. This enables the operating system to be reinstalled without the loss of personal files and settings, and makes it easier to backup system and user files. Another essential benefit of partitioning is that it allows Linux to have a dedicated area for virtual memory swapping. It is also common to have several partitions on a hard drive, each of which stores an operating system. This enables users to install and run multiple operating systems on a computer without using virtualization.
The process of partitioning a hard drive should not cause any data loss. However if anything goes wrong during the process, data can be lost. Consequently, it is always best to play safe and perform a full backup before tampering with partitions on a disk.
To provide an insight into the quality of software that is available, we have compiled a list of 5 high quality open source partition tools that offer an excellent way to create, destroy, resize, move, check and copy partitions.
Our recommendations are captured in this legendary LinuxLinks-style ratings chart. All software featured is free and open source.
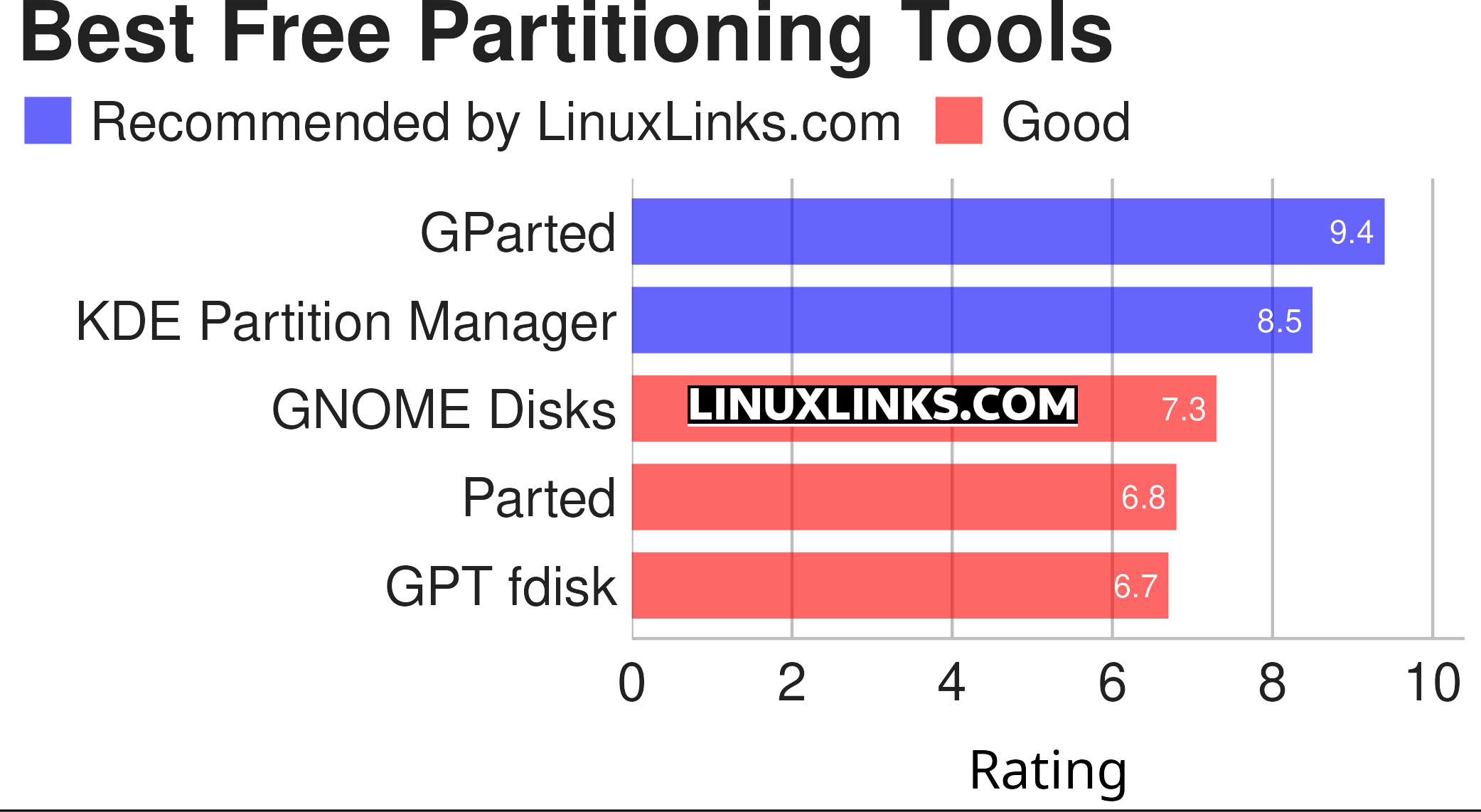
Click the links in the table below to learn more about each tool. A special mention goes to the util-linux package which includes the venerable fdisk and cfdisk tools.
| Partitioning Tools | |
|---|---|
| GParted | Popular partition editor for graphically managing your disk partitions |
| KDE Partition Manager | Disk partitioning application for the KDE Platform |
| GNOME Disks | The disk utility in GNOME |
| Parted | GParted and KDE Partition Manager use the Parted libraries |
| GPT fdisk | Set of text-mode partitioning tools |
This article has been revamped in line with our recent announcement.
 Read our complete collection of recommended free and open source software. Our curated compilation covers all categories of software. Read our complete collection of recommended free and open source software. Our curated compilation covers all categories of software. Spotted a useful open source Linux program not covered on our site? Please let us know by completing this form. The software collection forms part of our series of informative articles for Linux enthusiasts. There are hundreds of in-depth reviews, open source alternatives to proprietary software from large corporations like Google, Microsoft, Apple, Adobe, IBM, Cisco, Oracle, and Autodesk. There are also fun things to try, hardware, free programming books and tutorials, and much more. |
